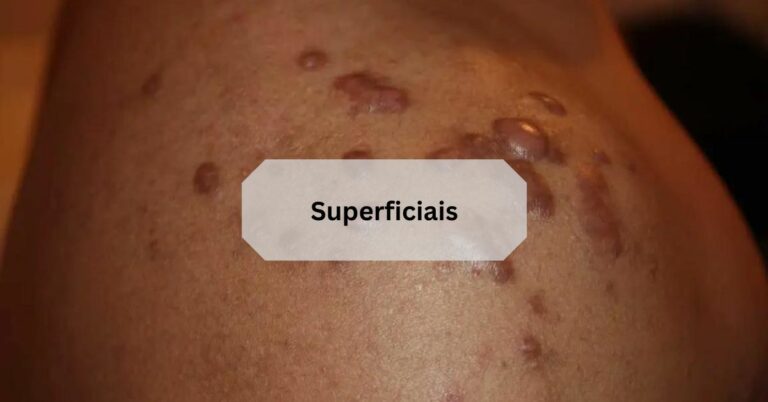
Superficiais, a common dermatological concern, encompass various skin lesions that affect the outermost layer of the skin, known as the epidermis.
Superficiais are shallow skin lesions affecting the epidermis, presenting as patches, bumps, or discolorations on the skin surface. They can vary in appearance and severity, often causing discomfort and aesthetic concerns.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of superficiais, exploring their definition, types, causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, preventive measures, and their impact on individuals’ lives.
Understanding Superficiais: What Are They?
Superficiais refer to shallow skin lesions that affect the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin.
These lesions may appear as patches, bumps, or discolorations on the skin surface.
They can vary widely in appearance and severity, often causing discomfort and aesthetic concerns.
Proper diagnosis and management are essential for effective treatment and improved quality of life.
Causes Of Superficiais:
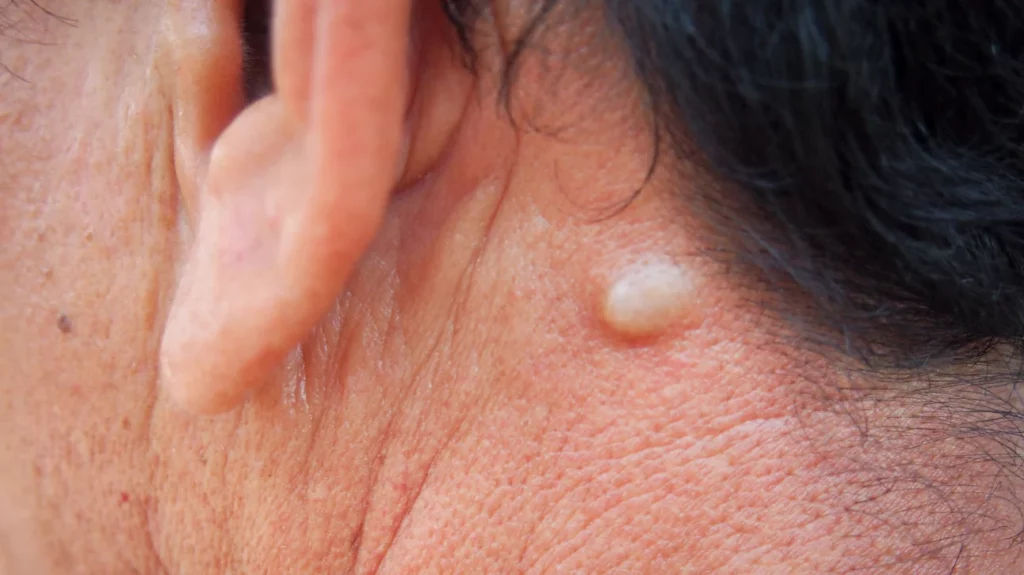
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from sunlight, pollution, and harsh chemicals can trigger superficial skin lesions.
- Genetic Predisposition: Some individuals may have a genetic predisposition to develop certain types of superficiais, such as melasma or vitiligo.
- Lifestyle Choices: Unhealthy lifestyle habits, such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and poor skincare routines, can exacerbate superficial skin conditions.
Symptoms And Signs Of Superficiais:
1. Visual Symptoms:
Individuals with superficiais may notice skin colour, texture, or overall appearance changes.
These changes can range from subtle discolorations to more noticeable patches or bumps on the skin surface.
Common visual symptoms include hyperpigmentation, where certain areas of the skin appear darker than the surrounding skin, or hypopigmentation, characterized by lighter areas of skin.
2. Sensory Symptoms:
In addition to visual symptoms, superficiais can cause sensory symptoms such as itching, burning, or discomfort.
These sensations may occur intermittently or persistently, especially when the lesions are exposed to environmental triggers or during inflammation.
Diagnosis Of Superficiais:
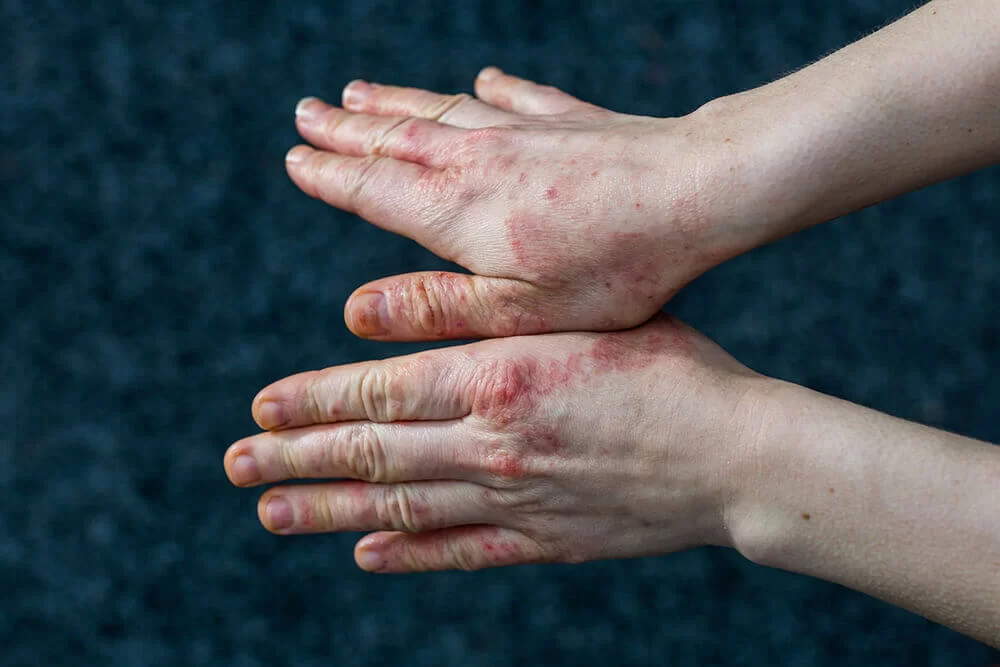
- Physical Examination: A dermatologist will thoroughly examine the affected skin to assess the type, location, and severity of superficies.
- Imaging Tests: In some cases, imaging tests such as dermoscopy or ultrasonography may be performed to evaluate the deeper layers of the skin and rule out other underlying conditions.
- Biopsy: A skin biopsy may be recommended to obtain a tissue sample for microscopic analysis, helping to confirm the diagnosis and guide treatment decisions.
Treatment Options For Superficiais:
- Topical Treatments: Topical medications, such as corticosteroids, retinoids, and hydroquinone, may be prescribed to reduce inflammation, lighten pigmentation, or improve skin texture.
- Oral Medications: In severe cases of superficiais, oral medications such as oral corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, or antimalarial drugs may target underlying inflammatory processes.
- Surgical Interventions: Surgical procedures, including laser therapy, cryotherapy, or chemical peels, may be recommended to remove superficial skin lesions or improve overall skin appearance.
Preventive Measures For Superficiais:
1. Sun Protection:
Regularly applying broad-spectrum sunscreen with a high SPF, wearing protective clothing such as hats and sunglasses, seeking shade during peak sun hours, and avoiding indoor tanning can help prevent superficial skin damage caused by UV radiation.
2. Healthy Lifestyle Choices:
Adopting a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, staying hydrated by drinking plenty of water, regular exercise to promote circulation and overall health, avoiding smoking, and limiting alcohol consumption can support overall skin health and reduce the risk of superficial skin conditions.
3. Skin Care Practices:
Establishing a consistent skincare routine that includes gentle cleansing, moisturizing, and non-comedogenic products can help maintain skin barrier function and minimize the risk of superficial skin lesions.
Additionally, avoiding harsh chemical products and abrasive exfoliants can prevent irritation and inflammation.
4. Avoiding Environmental Triggers:
Minimizing exposure to environmental factors such as pollution, harsh chemicals, and extreme temperatures can help reduce the risk of developing superficial skin lesions.
Using protective barriers such as gloves or barrier creams when handling irritants can also prevent skin damage.
5. Regular Skin Checks:
Regular self-examinations of the skin to monitor for any changes in moles, lesions, or discolorations can help detect superficial skin abnormalities early.
Seeking prompt medical evaluation for any suspicious or concerning skin changes is essential for timely diagnosis and treatment.
Complications Associated With Superficiais:
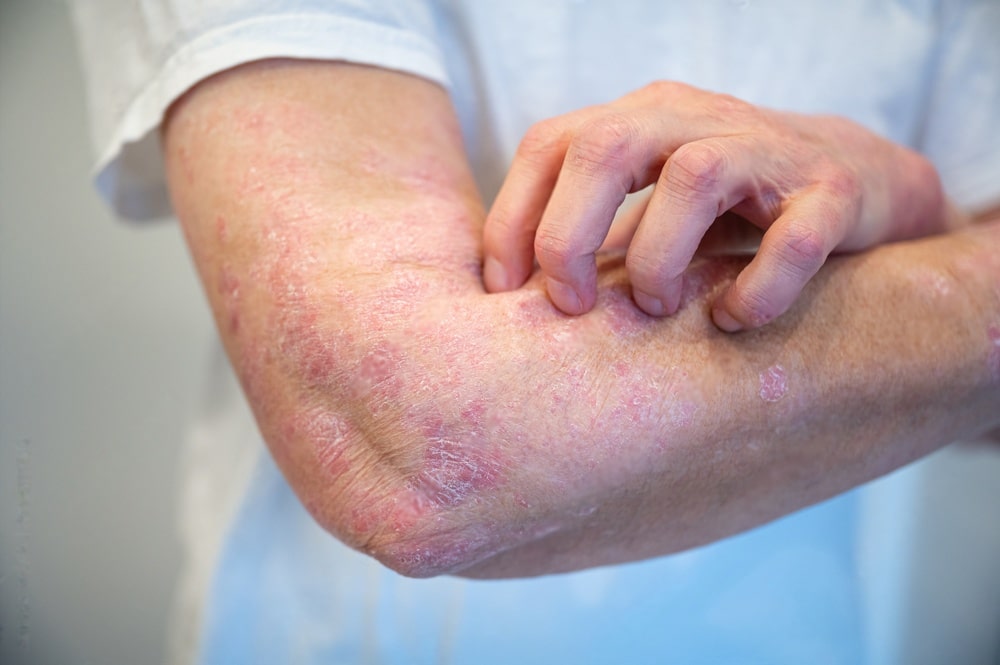
1. Infection Risks:
Open wounds or broken skin associated with superficiais lesions may increase the risk of bacterial, viral, or fungal infections, requiring prompt medical attention.
2. Scarring:
In some cases, superficial skin lesions may heal with scarring or permanent skin discolouration, mainly if not adequately treated or managed.
Research And Developments In Superficiais Management:
1. Advancements In Treatment Modalities:
Ongoing research and clinical trials are exploring novel treatment approaches, including targeted therapies, biologic agents, and stem cell-based therapies, for more effective management of superficiais.
2. Clinical Trials:
Participation in clinical trials offers opportunities to access cutting-edge treatments and contribute to advancing medical knowledge and treatment options for superficial.
Conclusion:
Superficiais are common dermatological conditions characterized by shallow skin lesions that can vary in appearance and severity. Understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for superficiais is essential for effective management and improved quality of life. By adopting preventive measures, seeking professional help, and staying informed about advancements in treatment modalities, individuals can better cope with superficiais and maintain healthy skin.
Related Questions:
1. Are Superficiais Contagious?
Superficiais themselves are not contagious, but certain underlying conditions or infections associated with superficial skin lesions may be infectious.
2. Can Superficiais Be Cured Completely?
The treatment and management of superficiais depend on the underlying cause and individual factors. While some superficial skin conditions can be effectively managed or improved, complete cure may not always be possible.
3. Are There Any Natural Remedies For Superficiais?
Some individuals may relieve superficial skin symptoms using natural remedies such as aloe vera, coconut oil, or vitamin E. However, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional before trying alternative treatments.
4. Can Superficiais Lead To Skin Cancer?
While superficial skin lesions themselves are typically benign, certain types of superficiais may increase the risk of developing skin cancer, especially if left untreated or if there is a history of sun damage.
5. How Long Does It Take To See Results From Superficial Treatments?
The timeline for seeing results from superficial treatments can vary depending on the type of treatment used, the severity of the condition, and individual factors. Some individuals may notice improvement within a few weeks, while others may require more extended treatment courses.
Read: